
- How to install virtualbox without gui how to#
- How to install virtualbox without gui 64 Bit#
- How to install virtualbox without gui serial#
- How to install virtualbox without gui manual#
- How to install virtualbox without gui iso#
Os="-os-type=linux -os-variant=centos7.0" Here is an example of what the script should look like: Now, download the OS you want to install, and then copy it to the folder shown below:Ĭp CentOS-7-x86_64-Everything-1708.iso /var/lib/libvirt/images/įinally, run virt-install. Yum install qemu-kvm qemu-img libvirt libvirt-python libvirt-client virt-install virt-viewer bridge-utils tigervnc-server In order to use virt-install, you need to install the following:
How to install virtualbox without gui how to#
Although you can use a VM to install another VM, you won't be able to connect to the VM within a VM unless you set up some kind of port forwarding and export the display - in other words, you'd have to understand how to get the X graphical protocol working across a network. Normally, you would use a host OS to install a VM.
How to install virtualbox without gui serial#
Another option is to use the ttyS0 serial interface to connect to the machine and complete those steps. You can either kick off the install and then finish with a GUI using a virtual network computing (VNC) client - like connecting to port 5900 - or you can use a kickstart file to answer all the questions that a GUI install would include, like keyboard type and language, time zone, and, for CentOS, whether to enable networking. Although there are additional use cases, these are the most common.īecause you have setup scripts, you can add them to your Puppet, Ansible or Salt systems and push VMs out from a centralized mechanism, albeit one that's less overarching than OpenStack. You can also set up a Xen hypervisor without having to use Xen-specific tools. This enables you to experiment with different virtualization technologies, like QEMU and KVM. Virt-install can also be used when you want to create a paravirtualized environment, which is a VM inside a VM - meaning one that is virtual and not hardware-based.

Also, you can use libvirt package templates as kickstart files, so once you decide on a configuration, you can copy it to other servers. This native Linux feature can also be used so you don't have to install Oracle VM VirtualBox, a VMware product or a third-party product. Once that is done, click on the green start arrow on the menu bar.įollow the steps described in the Installation Handbook, just as if you were installing Alpine on a real PC.Virt-install is used to roll out new VMs without having to use some large and complicated system like OpenStack.
How to install virtualbox without gui iso#
Select the entry “choose image” and open the Alpine ISO you downloaded earlier. One of the entries should read Mass storage, and offer an IDE controller with a primary master (the virtual hard disc) and a secondary master (the virtual optical drive).Ĭlick on the secondary master. Click on it for more information about your guest.

You will see a new entry in Virtual Box, called Alpine (or the name you chose during step 1 in the dialogue above).
How to install virtualbox without gui 64 Bit#
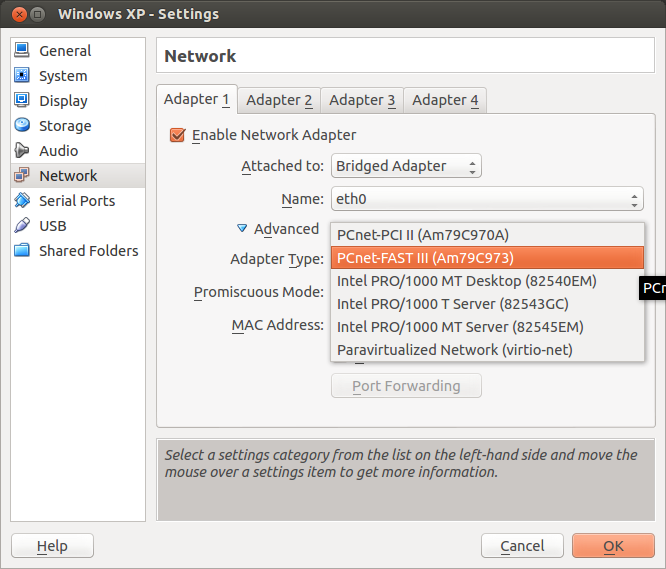
Choose 64 bit if you downloaded the x86_64 Alpine-ISO, or 32 bit if you downloaded the x86 Alpine-ISO.
How to install virtualbox without gui manual#
If you have problems, consult the VirtualBox user manual or one of the support sites for Virtual Box.ĭownload the Virtual Alpine ISO, which is optimized for virtual systems, from the Alpine Download section. Install both and start VirtualBox to check for proper operation.
Either from the official homepage (for Windows, OS X or Solaris) or from your distribution’s repository (for Linux). 3 Install Alpine on the virtual computerįirst you'll need to download and install Virtual Box on your host computer.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
